Lifecycle
Fairy's container will manage the lifecycle of the components, and it will be responsible for creating and destroying the components.
Launching
Here is few graph about how lifecycle works in a fairy plugin.
Plugin Lifecycle
| Life Cycle | Description |
|---|---|
| Plugin.onLoad() | The alternative of JavaPlugin.onLoad() |
| Plugin.onPreEnable() | The alternative of JavaPlugin.onEnable(), called before anything is initialized. |
| Launch Fairy Container | Initializing the container of the main fairy package. see Container Lifecycle. |
| Launch Plugin Container | Initializing the container of the plugin package, see Container Lifecycle. |
| Plugin.onPostEnable() | Called after everything is initialized. |
Container Lifecycle
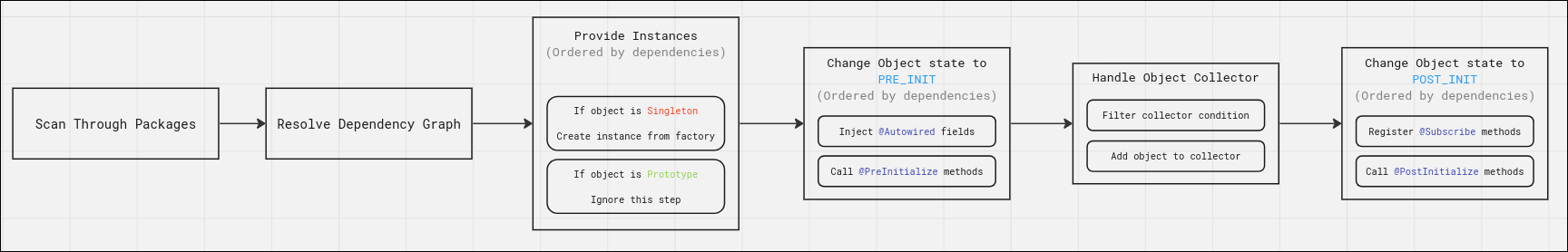
| Life Cycle | Description |
|---|---|
| Scan Through Packages | Class Scanner will scan through the specified package and cache them for launching. |
| Resolve Dependency Graph | Resolve dependencies depends on the way they are injected, see Dependencies. |
| Provide Instances | Provide instances for every object (injectable components) if they are singleton. if an object was prototype they won't be created by default unless they are dependent by other singleton. |
| Change Object state to PRE_INIT | The pre initialize state of the container, autowired fields will be injected and life cycle callback methods are called. |
| Handle Object Collector | Object collector active, every objects will be put into collectors and adds them depends on their condition. |
| Change Object state to POST_INIT | The post initialize state of the container, @Subscribe methods will be registered and life cycle callback methods are called. |
Callbacks
Fairy container provides a few callback methods that can be used to perform some actions when the container is initializing or destroying.
@PreInitialize Annotation
The @PreInitialize annotation is used to mark a method as a pre-initialize method. The method will be called before the object is fully initialized. (aka PRE_INIT state.)
@InjectableComponent
public class MyComponent {
@PreInitialize
public void onPreInitialize() {
// ...
}
}
@PostInitialize Annotation
The @PostInitialize annotation is used to mark a method as a post-initialize method. The method will be called after the object is fully initialized. (aka POST_INIT state.)
@InjectableComponent
public class MyComponent {
@PostInitialize
public void onPostInitialize() {
// ...
}
}
@PreDestroy Annotation
The @PreDestroy annotation is used to mark a method as a pre-destroy method. The method will be called before the object is destroyed. (aka PRE_DESTROY state.)
@InjectableComponent
public class MyComponent {
@PreDestroy
public void onPreDestroy() {
// ...
}
}
@PostDestroy Annotation
The @PostDestroy annotation is used to mark a method as a post-destroy method. The method will be called after the object is destroyed. (aka POST_DESTROY state.)
@InjectableComponent
public class MyComponent {
@PostDestroy
public void onPostDestroy() {
// ...
}
}
JSR-250 Annotations
Fairy also supports the JSR-250 annotations for lifecycle callbacks. The @PostConstruct and @PreDestroy annotations can be used to mark methods as post-initialize and pre-destroy methods.
@InjectableComponent
public class MyComponent {
@PostConstruct
public void onPostConstruct() {
// ...
}
@PreDestroy
public void onPreDestroy() {
// ...
}
}